JavaScript enabled Asynchronous programming to be easier to implement and understand. As a result, special Async and Await were introduced as keywords.
Let’s look at the reasons why they are employed.
Can utilize functions in various scenarios in which the execution of a function is contingent on the results of the previous function and needs to wait for it to be completed.
An easy illustration of this could be one of the most common examples is an API call. The information in the API call needs to be downloaded before performing other operations with it.
Async
An Async function is defined by including the Async keyword in the function. The function returns promises
It could be declared like this
const check = async () => {
console.log("Async method")
}Await
Await function is declared the same manner in the same way as the Async method by adding a keyword Await before the declaration of the function.
const check = await () => {
console.log("Async method")
}The word “await” must be declared in the Async function.
The wait keyword causes code execution to stop at the line where it is declared until the promise is completed. It does, however, stop it; the process of executing the code will continue on the line where it is declared. It doesn’t stop the execution of the code outside of the Async block.
Now that we can individually compose these tasks, let’s look at what we can accomplish using these functions.
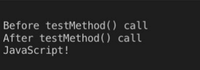
const testMethod = async () => {
const ret = await "JavaScript!"
console.log(ret);
}
console.log("Before testMethod() call")
testMethod()
console.log("After testMethod() call")Output



Leave a Reply